Because skin cancer can look different for each person, it is essential to be familiar with the causes and types of skin cancer. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, skin cancer is the growth of abnormal cells on the outermost skin layer, the epidermis. Cancers of the skin are the most common of all the types of cancer. The sun’s most harmful ultraviolet rays can be a cause of cancer along with the usage of UV tanning beds. Changes in an individual’s DNA sequence can also lead to skin cancer development. DNA changes can lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly, forming tumors.
Unlike cancers that develop inside the body, skin cancers form outside the epidermis and are usually visible. The good news is that skin cancer is generally curable if diagnosed and treated early. Learning to detect cancer early is critical, so looking for anything new, changing, or unusual on your skin is imperative. Dermatologists recommend scheduling an annual professional skin exam and checking your skin monthly to look for new and changing moles. Now that you know what causes skin cancer, let’s discuss one of the main types of skin cancer.
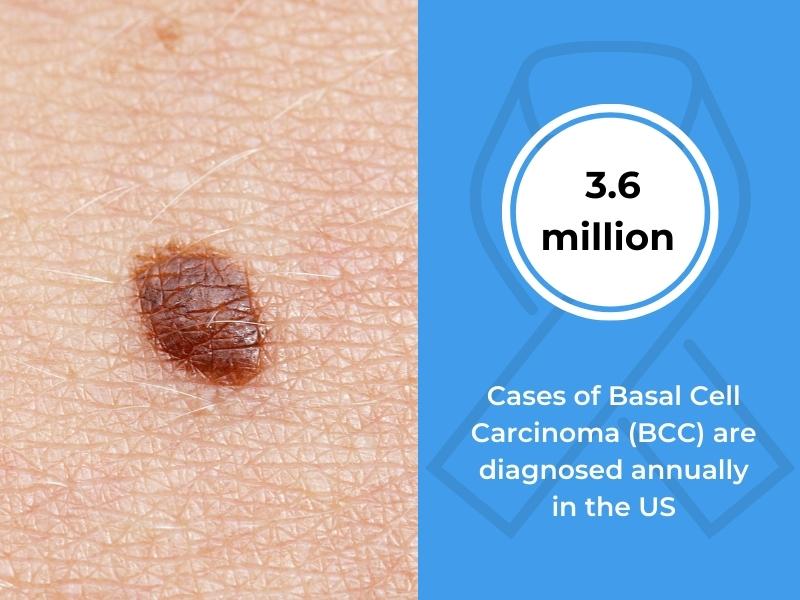
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is an abnormal growth that arises from the skin’s basal cells and is the most common form of skin cancer.. The function of basal skin cells is to produce new skin cells in the epidermis and usually develop on skin areas exposed to the sun, including the face, ears, neck, nose, shoulders, and back. It is recorded that 3.6 million cases of BCC are diagnosed annually in the US. This estimate equates to about 8 out of 10 basal cell cancers.
Ultraviolet UV Rays
Several risk factors make a person more likely to develop BCC. Exposure to the sun’s UV rays is a significant risk factor in developing skin cancer. The sun’s UV rays damage the DNA inside an individual’s skin cells. Here are factors that increase your skin cancer risk: UV exposure (sun or indoor tanning), a history of skin cancer, males over 50 years of age, fair skin, chronic infections, and inflammations. Ninety percent of nonmelanoma skin cancers are associated with exposure to the ultraviolet rays from the sun.
Light-colored Skin
While anyone can develop skin cancer, people with light-colored skin have a much higher risk than those with darker skin tones. People with darker skin have the skin pigment melanin, which acts as a protective layer. However, people with light-colored skin that freckles or burns are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
Albinism
Albinism is an inherited lack of protective skin pigment, which results in light-colored skin and a light hair color. This type of skin pigment is more sensitive to developing sunburns and skin cancers, so skin protection is highly advised.
Older
This risk of developing basal cell skin cancers does increase with age. This reason, explained by the American Cancer Society, is due to the buildup of sun exposure developed over time. However, skin cancers are becoming more common in younger people due to more time spent in the sun with exposed skin.
Male
The American Cancer Society reported that men are more likely than women to develop basal cell cancers of the skin due to the probability that men are getting more sun exposure.

Chemical exposure
The American Cancer Society describes that individuals who are or have been exposed to large amounts of arsenic (a natural element in rocks, soil, water, air, plants, and animals) can increase the risk of developing skin cancer. Exposure can come in many ways, including the environment (agricultural and industrial sources), food, work (exposure to copper or lead smelting, wood treatment, and glass manufacturing), and community where exposure to the above is relevant. Workers exposed to coal tar, paraffin, and certain petroleum products may also have an increased risk of skin cancer.
Radiation exposure
Individuals who have undergone radiation treatment have a much higher risk of developing skin cancer in the area treated.
Previous skin cancer
Individuals with BCC are at a much higher risk of developing another cancer.
Other risks
- Other risks include individuals with long-term skin inflammation or injury, including severe burns and skin damage by severe skin inflammatory diseases, which are more likely to develop skin cancers.
- Psoriasis treatment in the form of both Psoralens and ultraviolet light (PUVA) can also increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
- Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a rare inherited skin condition that reduces the ability of skin cells to repair DNA damage caused by sun exposure. Individuals with XP often develop many skin cancers.

Stages
Determining the stage of basal cell skin cancers is rarely needed since these are most always treated and cured by Dermatologist before spreading to other parts of the body.
Treatments for Basal Cell Cancers
There are several types of treatment available to remove or destroy BCC. The treatment options available depend on factors such as the tumor size and location, person’s age, health, and preferences. These types of cancers rarely spread to other parts of the body, however, they can grow into nearby tissues if not properly treated.
- Surgery including curettage and electrodesiccation, excision, Mohs surgery
- Radiation therapy for treating tumors on the eyelids, nose, or ears
- Immune response modifiers, photodynamic therapy, topical chemotherapy for very superficial tumors
- Cryotherapy is not recommended for large tumors on certain parts of the nose, ears, eyelids, scalp, or legs
- Targeted therapy or immunotherapy for advanced BCC can often shrink BCCs or slow their growth
For most individuals who have developed basal cell carcinoma, treatment often removes or destroys the cancer. For a small group of individuals with more advanced skin cancers, the cancer may not go away completely and may receive regular treatments of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or other treatments available to reduce the reoccurrence of the cancer. If you are diagnosed with a more aggressive type of skin cancer, it is imperative that a certified dermatologist treat that area.